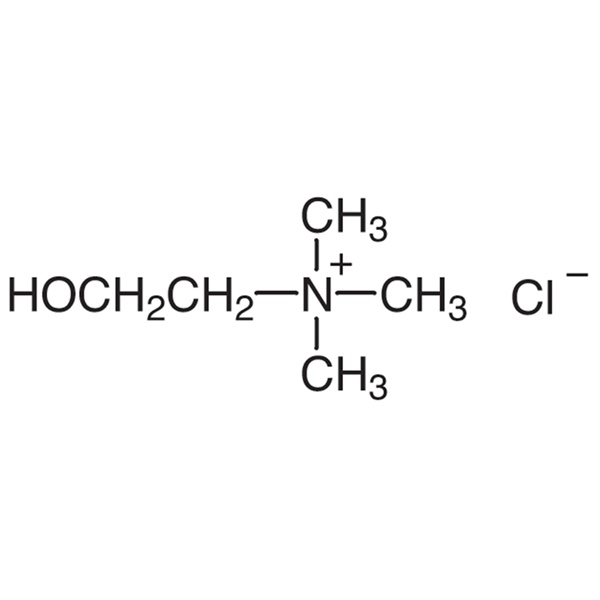
Choline Chloride CAS 67-48-1 Assay 99.0~100.5% (Titration)
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and supplier of Choline Chloride (CAS: 67-48-1) with high quality, commercial production. Ruifu Chemical can provide worldwide delivery, small and bulk quantities available, strong after-sale service. Welcome to order. Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | Choline Chloride |
| Synonyms | (2-Hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium Chloride |
| CAS Number | 67-48-1 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Capacity Thousands of Tons per Year |
| Molecular Formula | C5H14ClNO |
| Molecular Weight | 139.62 |
| Melting Point | 302.0~310.0℃ (dec.) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in Water |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with Strong Oxidizing Agents, Moisture. Store Under a Dry Atmosphere. |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Origin | Shanghai, China |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Item | Specifications | Specifications |
| Appearance | White Crystalline Powder | White Crystalline Powder |
| Identification A,B | Qualified | Qualified |
| Assay (Titration With AgNO3) | 99.0~100.5% (on Anhydrous Basis) | 99.35% |
| Melting Point | 302.0~310.0℃ | 302.0~305.0℃ |
| Water | ≤0.50% | 0.21% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.05% | 0.01% |
| 1,4-Dioxane | ≤10 µg/g | Passes Test |
| Ammonium, Volatile Amines | Passes Test | Passes Test |
| Single Impurity | ≤0.30% | <0.30% |
| Total impurities | ≤2.00% | <2.00% |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤2ppm | <2ppm |
| Lead (Pb) | <2mg/kg | 0.5mg/kg |
| Heavy Metals (as Pb) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
| Solubility in Water | Pass 500 mg/ml in H2O | Pass |
| pH (10% Solution) | 4.0~7.0 | 4.0~7.0 |
| Total Plate Count | <1000cfu/g | <10cfu/g |
| Yeast & Mold | <100cfu/g | <10cfu/g |
| Salmonella | Negative | Negative |
| E.Coli | Negative | Negative |
| Conclusion | Qualified, Conform to FCCV | Qualified |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
1, Choline Chloride storage temperature should not be lower than -12℃, in order to avoid blocking the pipeline after crystallization.
2, Choline Chloride powder storage in the silo should use dehumidification equipment to prevent product moisture absorption. The choline chloride powder will cause the product to become wet and agglomerate after moisture absorption, resulting in blockage of the catheter. Plant carrier choline chloride powder may be fermented after long-term moisture absorption.
Choline Chloride
C5H14ClNO 139.62
(2-Hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium chloride;
2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride [67-48-1].
DEFINITION
Choline Chloride contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 100.5% of choline chloride (C5H14ClNO), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption <197K>
• B. Identification Tests-General, Chloride <191>: A solution (1 in 20) meets the requirements.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample: 120 mg
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry <541>.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N silver nitrate VS
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Blank: 35 mL of water. Add 3 drops of acetic acid.
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 35 mL of water and add 3 drops of acetic acid. Titrate with Titrant.
Calculate the percentage of choline chloride (C5H14ClNO) in the Sample taken:
Result = [(V B) × N × F × 100]/W
V = Sample titrant volume (mL)
B = Blank titrant volume (mL)
N = titrant normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 139.6 mg/mEq
W = weight of the Sample (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%-100.5% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
• Residual Solvents <467>: Meets the requirements, except that the limit for 1,4-dioxane is 10 µg/g
• Residue on Ignition <281>: NMT 0.05%
• Arsenic, Method I <211>
Analysis: Add 30 mL of water and 5 mL of hydrochloric acid to dissolve the sample.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 2 ppm
• Lead <251>
[Note-Use methylene chloride in place of chloroform to prepare the Dithizone Extraction Solution and Standard Dithizone Solution. ]
Solution A: Transfer 8.4 g of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 2) to a plastic bottle, add 100 mL of ammonium hydroxide, and mix.
Standard solution: Transfer 1.0 mL of the Diluted Standard Lead Solution to a separatory funnel containing 25.0 mL of water.
Sample solution: Dissolve 3.00 g of Choline Chloride in a separatory funnel containing 25.0 mL of water.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Separately add 6.0 mL of Ammonium Citrate Solution and 3.0 mL of Potassium Cyanide Solution to the Standard solution and the Sample solution. Extract each of the resulting solutions three times with 5.0-mL portions of Dithizone Extraction Solution, shaking for 60 s and draining off each extract into another separator. Shake the combined dithizone solutions for 30 s with 20.0 mL of nitric acid (1 in 100), and discard the methylene chloride layer. Add 6.0 mL of Ammonia–Cyanide Solution, 2 mL of Solution A, and 10 mL of Standard Dithizone Solution, and shake for 45 s. Allow the phases to separate, and measure the absorbance of the lower layer at 510 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer.
Acceptance criteria: The absorbance of the Sample solution is NMT the absorbance of the Standard solution (NMT 0.3 ppm).
• Heavy Metals, Method II <231>: NMT 10 ppm
• Limit of Total Amines
Standard solution: 500 µg/mL of trimethylamine hydrochloride in water
Sample solution: Transfer 10.0 g of Choline Chloride to a beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar, add 170 mL of water and 30.0 mL of sodium hydroxide TS, and stir until dissolved.
System suitability stock solution: 10 µg/mL of trimethylamine hydrochloride in water
System suitability solution: Transfer 10.0 mL of System suitability stock solution to a beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar, add 160 mL of water and 30.0 mL of sodium hydroxide TS, and stir until dissolved.
Electrode system: Use a gas-sensing, ammonia-specific indicating electrode with internal reference connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials with a minimum reproducibility of ±0.1 mV (see pH 791).
Standard response line: Mix 30.0 mL of sodium hydroxide TS, and 170 mL of water. Add a plastic-coated stirring bar, insert the electrode into the solution, and record the potential, in mV. Continue stirring, and at 5-min intervals add 0.200, 0.600, 1.00, and 2.00 mL of Standard solution, and record the potential after each addition. Plot the logarithms of the cumulative trimethylamine hydrochloride concentrations (0.50, 1.50, 2.50, and 5.00 µg/mL) versus potential, in mV, and determine the slope (S) of the Standard response line for the electrode.
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Proceed as directed in Analysis, except to replace the Sample solution with the System suitability solution and in the formula below to replace W with V, which equals 10 mL.
Suitability requirements: The total change is NLT 10 mV for a 0.4-mL cumulative addition of the Standard solution; the amount of trimethylamine hydrochloride found is 8.5-11.5 µg/L.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Rinse the electrode, insert it into the Sample solution, stir, and record the potential, in mV. Add 0.100 mL of the Standard solution, and record the potential. Add another 0.100 mL of the Standard solution, and record the potential. [Note—If the total change after the second addition of the Standard solution is less than 10 mV, add a third aliquot of 0.200 mL.]
Calculate the content, in µg/g, of total amines as trimethylamine hydrochloride in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (CS × VA)/[(F 1) × W]
CS = concentration of Standard solution (µg/mL)
VA = total volume of the Standard solution added to the Sample solution (mL)
W = weight of Choline Chloride taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
F = correction factor, calculated by the formula:
F = antilog [(mVF mV0)/S]
mVF = final reading after the additions of the Standard solution (mV)
mV0 = initial reading of the Sample solution (mV)
S = slope of the Standard response line for the electrode
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 µg/g
• Chromatographic Purity
Buffer solution: 7.1 g/L of anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.5.
Mobile phase: Buffer solution and acetonitrile (7:3)
Standard solution: Transfer an amount, NMT 100 mg, of USP Choline Chloride RS to a 24-mL screw-capped vial, and add 400 mg of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and 10 mL of acetonitrile. Cap the vial, heat to 55, and continue heating for 2 h. Cool to room temperature, and add 5 mL of water. Allow to stand for 5 min. Quantitatively transfer the solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with acetonitrile to volume. Dilute a volume of this solution with Mobile phase to obtain a concentration of 2.0 µg/mL of USP Choline Chloride RS.
Sample solution: Transfer 110 mg of Choline Chloride to a 24-mL screw-capped vial. Dry at 120 for 2 h. Add 400 mg of 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and 10 mL of acetonitrile. Cap the vial, heat to 55, and continue heating for 2 h. Cool to room temperature, and add 5 mL of water. Allow to stand for 5 min. Quantitatively transfer the solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Pipet 2.0 mL of the solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography <621>, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 208 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L7
Column temperature: 30
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Capacity factor (k'): NLT 2
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5%, determined from the choline derivative peak
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Choline Chloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
rU = peak response for each impurity, excluding that for the choline derivative and 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid from the Sample solution
rS = peak response for the choline derivative from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Choline Chloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Choline Chloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities: NMT 0.3%
Total impurities: NMT 2.0%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• pH <791>: 4.0-7.0, in a solution (1 in 10)
• Water Determination, Method I <921>: NMT 0.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers.
• USP Reference Standards <11>
USP Choline Chloride RS

Hazard Symbols Xi - Irritant
Risk Codes
36/37/38 - Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
Safety Description
S26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36 - Wear suitable protective clothing.
WGK Germany 1
RTECS KH2975000
FLUKA BRAND F CODES 3-9
TSCA Yes
HS Code 2923100000
Choline Chloride (CAS: 67-48-1) is the most commonly used as well as most economical form of synthetic choline and is a water soluble vitamin, and is the component for constituting of acetylcholine, lecithin, and nerve phospholipids of biological tissue. Moreover, Choline Chloride can save methionine and is an important material required for livestock, poultry, and fish. As a kind of feed additive, Choline Chloride has the following physiological effects: Choline Chloride can prevent the accumulation of the fat in liver and the kidney and tissue degeneration; it can promote recombination of amino acids; it can improve the utilization efficiency of amino acids, especially the essential amino acid methionine in vivo. It can be used for treating fatty liver and cirrhosis. Choline Chloride can be used as the feed additive which is capable of stimulating ovaries for giving birth to more eggs and farrowing. It can also facilitate the weight gaining process of livestock, fish, etc. Choline Chloride was developed by the Agricultural Technology Institute of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan in 1964 and registered as a plant growth regulator in 1987, also became vitamin B4.
Drugs
Choline Chloride can be used to treat fatty liver and cirrhosis.
Choline can promote fat metabolism in the liver and kidney; Choline is also the basis of the body's synthesis of acetylcholine, thus affecting the transmission of nerve signals. In addition, choline is also one of the methyl sources required for methionine synthesis in vivo.
Feed Additive
Choline Chloride can effectively prevent and treat fat deposition and tissue degeneration in livestock and poultry organs. Can promote the absorption and synthesis of amino acids. It can enhance the health and disease resistance of livestock and poultry, promote the growth and development, and improve the Laying rate of poultry. Dosage 1~2g/kg.
Also as livestock feed additives, can stimulate the ovary more egg, litter and livestock, fish and other weight gain. Natural choline is found in many foods, but its concentration is insufficient to meet the needs of the modern feed industry for the rapid growth of animals. Therefore, synthetic choline should be added to feed to meet its needs. Lack of choline can lead to fatty liver, slow growth, decreased egg production, increased death and other phenomena.
Agricultural Crop Promoter
Choline Chloride is also a plant photosynthesis promoter, which has obvious effect on increasing yield. Spraying at the booting stage of wheat and rice can promote the differentiation of spikelet, multiple ear grains, and the spraying at the filling stage can speed up the filling rate, the ear grains are full, and the weight of thousand grains is increased by 2~5 grams.
Can also be used for corn, sugarcane, sweet potato, potato, radish, onion, cotton, tobacco, vegetables, grapes, mango, etc, the effect is stable under the condition of ecological environment. In the early stage of expansion of the root and other underground part of the growing crops, 10~20 ml of 60% water agent per mu (6~12g of active ingredient) is used, add water 30 liters dilution (1500~3000 times), spraying 2~3 times, the expansion and yield increase effect is obvious; Ornamental plants rhododendron, euphorbia, geranium, hibiscus regulate growth; Wheat, barley, oat lodging resistance.
-
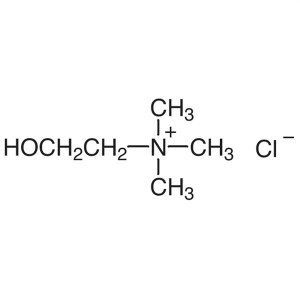
Choline Chloride CAS 67-48-1 Assay 99.0~100.5% ...
-
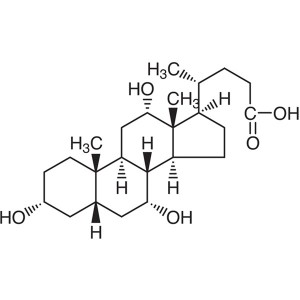
Cholic Acid CAS 81-25-4 Purity >98.0% (HPLC) Fa...
-
Citicoline CAS 987-78-0 CDP-Choline Purity ≥99....
-
Citicoline Sodium Salt Hydrate CAS 33818-15-4 A...
-
3α-Hydroxy-7-oxo-5β-Cholanic Acid CAS 4651-67-6...
-
Acetylcholine Chloride CAS 60-31-1 Assay 98.0~1...
-
Choline Glycerophosphate CAS 28319-77-9 Assay 9...
-
Choline Hydroxide Solution CAS 123-41-1 44 wt. ...
-
Phosphocholine Chloride Calcium Salt Tetrahydra...